比较重要的图论,tg 中考得比较多。
1. 定义
连通分量:可以互相到达的点集
强连通分量:极大的连通分量(即不可扩展的)
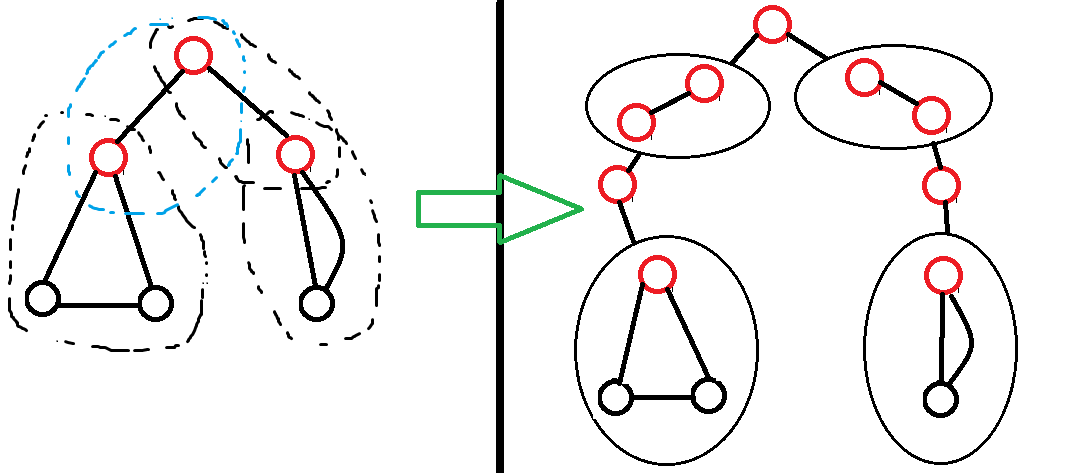
常见应用:缩点,可将有向图变为有向无环图( DAG ),无向图变为树 / 森林。
2. 求强连通分量( SCC ): DFS+Tarjan 注意,下面的定义是属于有向图的,无向图等一下再讨论!
1) DFS 的特殊定义 边可分为4类:
树枝边:搜索时所经历的边(树枝边构成树)
前向边:祖先指向儿子
后向边:儿子指向祖先
横叉边:不属于上面3种的边 ( 大雾 )
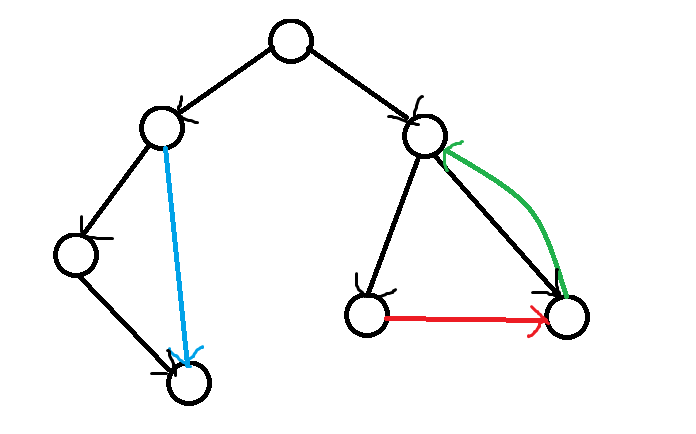
(黑色为树边,蓝色为前向边,红色为橫叉边,绿色为后向边)
2) 哪些边有用?
后向边:祖先先到儿子,儿子回到了祖先(一定是)
横叉边:点先到另外点,在有横叉边的话可能回到了祖先
3) Tarjan 算法 a. 又是定义( 雾 )
时间戳( dfn ):遍历到 u 的时间点
low :以 u 为根的子树,只走一条边能到达的 dfn 的最小值
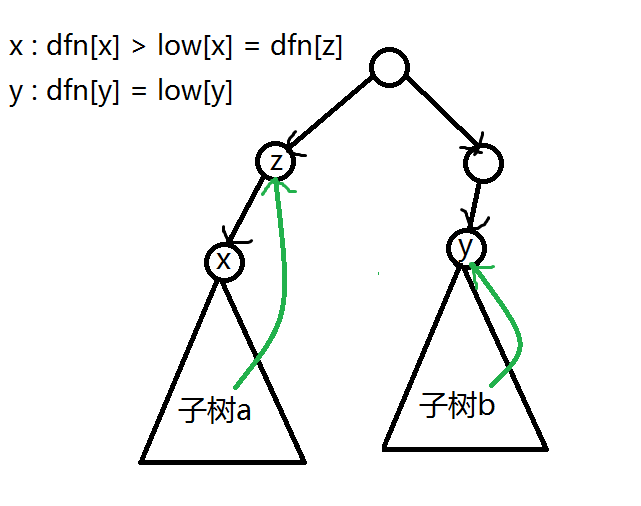
u 是一个强连通分量 dfn 的最小值,等价于 $dfn(u) = low(u)$
b. 算法流程
保存一个栈,是搜到的点
搜索所有相邻的点,如果未搜过,就递归搜索,如果搜过(即不是树枝边),就有 $low(u)=\min (dfn(v),low(u))$
如果 $dfn(u) = low(u)$,将栈里的点一一取出,合并为一个 SCC,直到取出自己
复杂度 $O(m+n)$
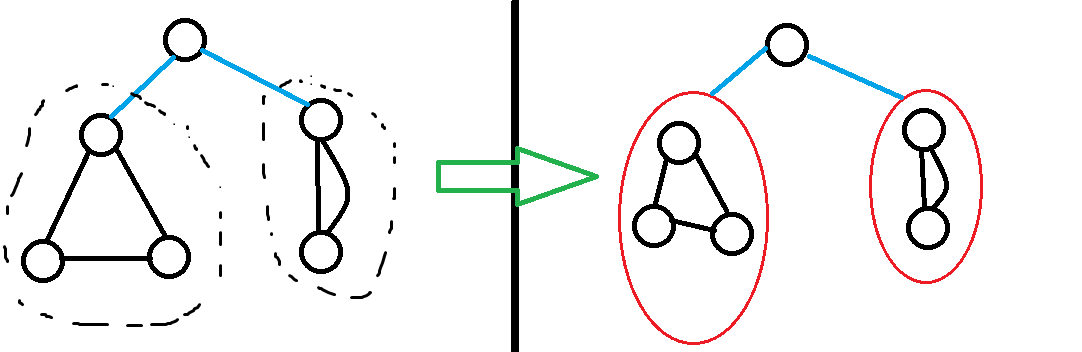
c.证明:略(过于复杂) 3. 后续事务 1) 缩点 遍历每一条原图中的边,如果端点不在同一分量中,就将该两个 SCC 连起来
2) 在 DAG 上拓扑排序 其实可以不用,因为 SCC 的顺序就是拓扑序的倒序
证明: 拓扑序的第一个,一定会在搜的时候搜到其他的强连通分量,并在该 SCC 前就已经结束,第一个一定是最后搜到的 SCC
4. Code 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 void Tarjan (int x) dfn[x]=low[x]=++tot; st[++top]=x, ins[x]=true ; for (int i=h[x];~i;i=ne[i]) if (!dfn[e[i]]) { Tarjan (e[i]); low[x]=min (low[x],low[e[i]]); } else if (ins[e[i]]) low[x] = min (low[x], dfn[e[i]]); if (low[x]!=dfn[x]) return ; cnt++;int now; do { now=st[top--]; ins[now]=false ; bel[now]=cnt; }while (now!=x); return ; } void suodian () for (int x=1 ;x<=n;++x) for (int i=h[x];~i;i=ne[i]) if (bel[x]!=bel[e[i]]) add (h2, bel[x], bel[e[i]]); n=cnt; }
5. 无向图 既和有向图类似,有和有向图有区别。
首先,边的分类只有 3 种:树边,前向边,后向边。
为什么没有横叉边呢?其实原因很简单,首先,横叉边是指不同子树之间的边。试想,如果有横叉边的话,当我们走到先遍历的点 $u$ 时,另一个子树还没有遍历,那 $u$ 一定会走到 $v$,让横叉边变为了树边了。
注意,这个代码还应该传一个 $fa$,,防止又走回 $fa$ 而导致死循环了。
代码(找不到了……
6. 点双联通分量与边双连通分量 这两个有区别,一般用于无向图。
1)定义
点双连通分量:不存在割点,也就是任意去掉一个点,原图仍然联通。
边双连通分量:不存在桥,也就是任意去掉一条边,原图仍然联通。
还要区分的是,点双连通分量与边双连通分量是互不包含的,这个有些书上可能是讲错了。
2)判定
割点:存在一个点 $v$,使得 $dfn(u)\leq low(v)$(dfs 树的根节点需要两个 $v$),那么 $u$ 是割点。
桥:存在一条边 $e(u,v)$,使得 $dfn(u)<low(v)$,那么 $e(u,v)$ 是桥。
注意两个的判定区别。
3)简要证明
割点:因为 $v$ 所在的子树不可能到达 $u$ 以上的节点了,所以每一个节点向上遍历的话都要经过 $u$,所以 $u$ 删去后会使原图不联通。但如果是根节点的话,没有向上的点了,所以需要多一个 $v$,那么删去根节点后就不联通了。
桥:$v$ 所在的子树不可能到达 $u$ 及以上的节点了,所以删去 $e(u,v)$ 会使 $v$ 的子树与其他不联通, $e(u,v)$ 就是桥了。
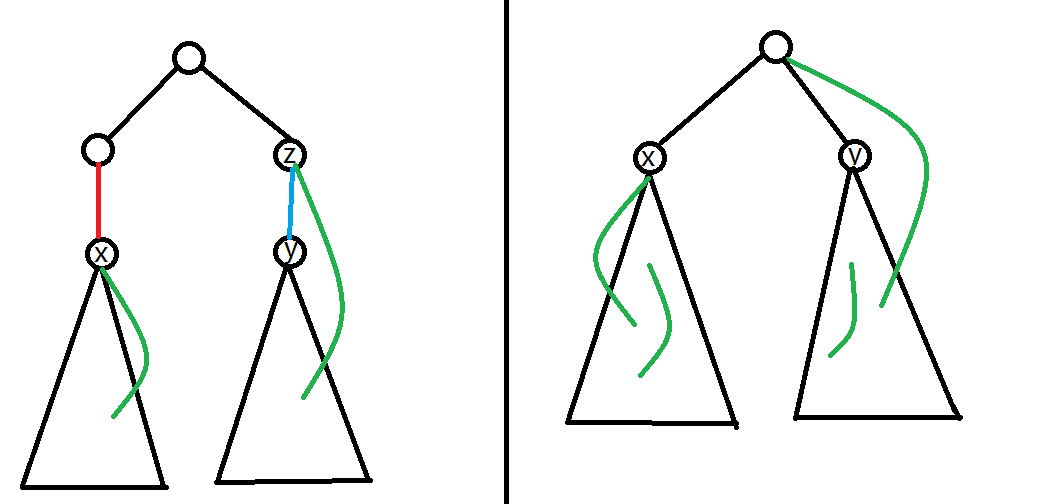
左边的图中,红色的边下面的点 $low(x)=dfn(x)$,$low(x)<dfn(x.fa)$,那么红边就是桥,但 $low(y)=dfn(z)\not<dfn(z)$,所以蓝边 $e(y,z)$ 不是桥。在右边的图中,$x$ 下面的点 $v$ 一定满足 $low(v)\geq dfn(x)$,所以 $x$ 就是割点。而 $y$ 下面的点会有 $low(x)=dfn(root)<dfn(y)$,所以 $y$ 就不是割点。
4)缩点 a. 边双连通分量 这个要简单一些,所以先讲(?
根据定义,不存在桥的子图就是边联通图,而极大的边联通图就是边双连通分量。
(其实和前面的 Tarjan 差不多)(废话,前面的无向图 Tarjan 就是边双连通分量)
b. 点双连通分量 这个其实要难一些 很多
首先,我们将所有的割点处理出来。
如果我们得到 $dfn(u)\leq low(v)$,我们就将当前栈内的所有点一直弹出,直到弹出的点为 $u$,将所有弹出的点都加入一个新的点双连通分量,然后还要将 $u$ 入栈。
如果要缩为一个新图的话,我们还要注意:每一个割点都是一个新图中的点,然后每一个点双连通分量也是新图中的一个点,连接就是割点向有它的点双连通分量连边。原图最后变为了一棵树(森林)。
缩完点后,就可以树形 DP 了。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 int h1[N], h2[N], e[M], ne[M], w[M], idx;int low[N], dfn[N], tot, stk[N], top, cnt;vector <int > dcc[N]; void add (int *h, int a, int b) e[idx] = b, ne[idx] = h[a], h[a] = idx ++; } void tarjan (int x, int from) low[x] = dfn[x] = ++ tot, stk[++ top] = x; for (int i = h[x]; ~i; i = ne[i]) { if (i == (from ^ 1 )) continue ; if (!dfn[e[i]]) { tarjan (e[i], i); if (low[e[i]] <= dfn[x]) { int now;cnt ++; while (stk[top] != x) { now = stk[top --]; dcc[cnt].push_back (now); } dcc[cnt].push_back (x); add (h2, x, cnt + n); } low[x] = min (low[x], low[e[i]]); } else low[x] = min (low[x], dfn[e[i]]); } }
7. 例题 T1: Luogu P2341 受欢迎的牛 题目传送门
如果是一个 DAG 的话,直接是出度为 0 的点就是答案
但是,如果有多个点的话,那么哪个点都不是。
考虑 Tarjan,缩点后出度为 0 的点的大小就是了。
Code:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 #include <iostream> #include <cstring> #include <cstdio> #include <algorithm> using namespace std;const int N=1e4 +10 ,M=5e4 +10 ;int h[N],e[M],ne[M],idx;int st[N],top,dfn[N],low[N],bel[N],cnt,tot,dout[N],din[N],n,m,s[N];bool ins[N];void add (int a,int b) e[idx]=b,ne[idx]=h[a],h[a]=idx++; } void Tarjan (int x) dfn[x]=low[x]=++tot; st[++top]=x, ins[x]=true ; for (int i=h[x];~i;i=ne[i]) if (!dfn[e[i]]) { Tarjan (e[i]); low[x]=min (low[x],low[e[i]]); } else if (ins[e[i]]) low[x] = min (low[x], dfn[e[i]]); if (low[x]!=dfn[x]) return ; cnt++;int now; do { now=st[top--]; ins[now]=0 ; bel[now]=cnt; s[cnt]++; }while (now!=x); return ; } int main () memset (h,-1 ,sizeof h); cin>>n>>m; int x,y; while (m--) { scanf ("%d %d" ,&x,&y); add (x,y); } for (int i=1 ;i<=n;++i) if (!dfn[i]) Tarjan (i); for (int x=1 ;x<=n;++x) { for (int i=h[x];~i;i=ne[i]) if (bel[x]!=bel[e[i]]) { dout[bel[x]]++; din[bel[e[i]]]++; } } int b=0 ; for (int i=1 ;i<=cnt;++i) { if (!dout[i]) { if (b) { puts ("0" ); return 0 ; } b=s[i]; } } cout<<b<<endl; return 0 ; }
T2: AcWing 367 学校网络 / Luogu P2812 校园网络(加强版) 题目传送门_AcWing
题目传送门_Luogu
对于第一问,缩点后,入度点的个数即为答案(这些点必须得到,得到后,所有也都会得到)
对于第二问,设入度为0的点有 $P$ 个,出度为0的点有 $Q$ 个,则答案为
证明有很多有些问题,这篇博客证明了(我也不知道有没有问题 雾 )
证明
Code:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 #include <iostream> #include <cstring> #include <cstdio> #include <algorithm> using namespace std;const int N=1e4 +10 ,M=5e6 +10 ;int h[N],e[M],ne[M],idx;int st[N],top,dfn[N],low[N],bel[N],cnt,tot,dout[N],din[N],n;bool ins[N];void add (int a,int b) e[idx]=b,ne[idx]=h[a],h[a]=idx++; } void Tarjan (int x) dfn[x]=low[x]=++tot; st[++top]=x, ins[x]=true ; for (int i=h[x];~i;i=ne[i]) if (!dfn[e[i]]) { Tarjan (e[i]); low[x]=min (low[x],low[e[i]]); } else if (ins[e[i]]) low[x] = min (low[x], dfn[e[i]]); if (low[x]!=dfn[x]) return ; cnt++;int now; do { now=st[top--]; ins[now]=0 ; bel[now]=cnt; }while (now!=x); return ; } int main () memset (h,-1 ,sizeof h); cin>>n; int x; for (int i=1 ;i<=n;++i) { while (cin>>x,x) add (i,x); } for (int i=1 ;i<=n;++i) if (!dfn[i]) Tarjan (i); for (int x=1 ;x<=n;++x) { for (int i=h[x];~i;i=ne[i]) if (bel[x]!=bel[e[i]]) { dout[bel[x]]++; din[bel[e[i]]]++; } } int a=0 ,b=0 ; for (int i=1 ;i<=cnt;++i) { if (!dout[i]) a++; if (!din[i]) b++; } cout<<b<<endl; if (cnt==1 ) puts ("0" ); else cout<<max (a,b)<<endl; return 0 ; }